Shoulder Rotation in Dog Pose and Full Arm Balance
External rotation of the humerus in overhead motion is important for gaining the full range of motion and avoiding impingment of the greater tuberosity of the humerus on the undersurface of the acromion. We illustrate this here for two common poses. To read more about the skeletal anatomy and subacromial impingement, click here for The Daily Bandha.
Here’s the Anatomy of the Rotator Cuff . . .
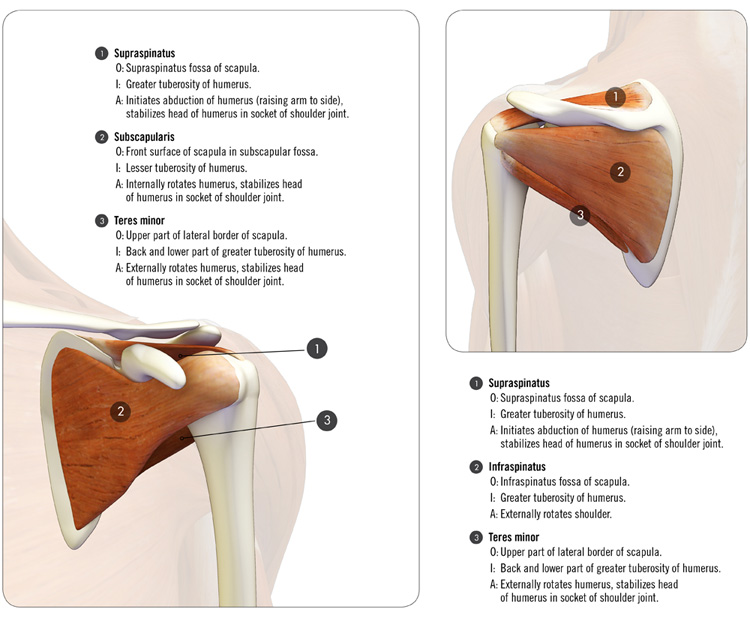
The rotator cuff is composed of four muscles. On the front is the subscapularis, which originates from the subscapular fossa of the scapula and inserts onto the lesser tuberosity of the humerus. This muscle acts to internally rotate the humerus at the shoulder. The supraspinatus originates from the supraspinous fossa of the scapula and inserts onto the greater tuberosity of the humerus. It acts to abduct the humerus and stabilize the humeral head in the glenoid (socket). The infraspinatus originates from the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and inserts onto the greater tuberosity of the humerus. It acts to externally rotate the humerus and depress the humeral head in the socket. The teres minor originates from the lateral border of the scapula and inserts onto the greater tuberosity of the humerus. It acts to externally rotate the humerus and has a minor function of adduction.
 And the Deltoid . . .
And the Deltoid . . .
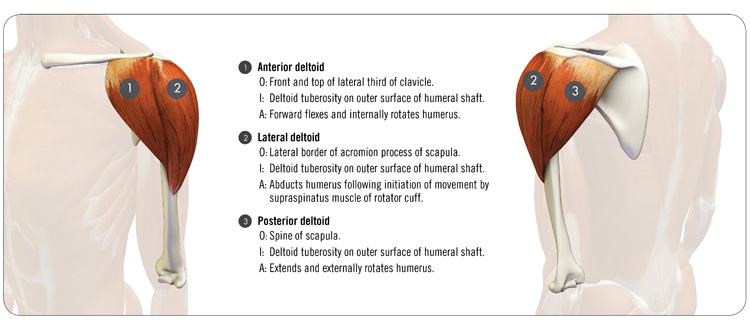
The deltoid muscle is divided into three parts: an anterior or front third, a middle or lateral third, and a posterior third. All three parts of this muscle converge to insert onto the deltoid tuberosity on the side of the humerus. The anterior part originates from the front of the acromion and the lateral third of the clavicle. It acts to elevate the humerus in the front of the body and synergizes internal rotation of the arm. The middle third originates from the lateral border of the acromion and acts to abduct the humerus. The posterior third originates from the spine of the scapula and acts to extend the arm back away from the body. It also synergizes external rotation of the arm.
 Dog Pose
Dog Pose
Externally rotate the shoulders in Dog Pose by engaging the infraspinatus and teres minor muscles. The posterior deltoids contribute to this action. Combine this with pronating the forearms and spreading the weight evenly across the palms of the hands. Then press forward into the hands as if you were trying to raise them overhead. They obviously will not raise, but this cue draws the trunk deeper into the pose. Externally rotating the shoulders first protects against subacromial impingement.
External rotation of the humerus in overhead motion is important for gaining the full range of motion and avoiding impingment of the greater tuberosity of the humerus on the undersurface of the acromion. We illustrate this here for two common poses. To read more about the skeletal anatomy and subacromial impingement, click here for The Daily Bandha.
Here’s the Anatomy of the Rotator Cuff . . .
The rotator cuff is composed of four muscles. On the front is the subscapularis, which originates from the subscapular fossa of the scapula and inserts onto the lesser tuberosity of the humerus. This muscle acts to internally rotate the humerus at the shoulder. The supraspinatus originates from the supraspinous fossa of the scapula and inserts onto the greater tuberosity of the humerus. It acts to abduct the humerus and stabilize the humeral head in the glenoid (socket). The infraspinatus originates from the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and inserts onto the greater tuberosity of the humerus. It acts to externally rotate the humerus and depress the humeral head in the socket. The teres minor originates from the lateral border of the scapula and inserts onto the greater tuberosity of the humerus. It acts to externally rotate the humerus and has a minor function of adduction.
 And the Deltoid . . .
And the Deltoid . . . The deltoid muscle is divided into three parts: an anterior or front third, a middle or lateral third, and a posterior third. All three parts of this muscle converge to insert onto the deltoid tuberosity on the side of the humerus. The anterior part originates from the front of the acromion and the lateral third of the clavicle. It acts to elevate the humerus in the front of the body and synergizes internal rotation of the arm. The middle third originates from the lateral border of the acromion and acts to abduct the humerus. The posterior third originates from the spine of the scapula and acts to extend the arm back away from the body. It also synergizes external rotation of the arm.
 Dog Pose
Dog Pose Externally rotate the shoulders in Dog Pose by engaging the infraspinatus and teres minor muscles. The posterior deltoids contribute to this action. Combine this with pronating the forearms and spreading the weight evenly across the palms of the hands. Then press forward into the hands as if you were trying to raise them overhead. They obviously will not raise, but this cue draws the trunk deeper into the pose. Externally rotating the shoulders first protects against subacromial impingement.
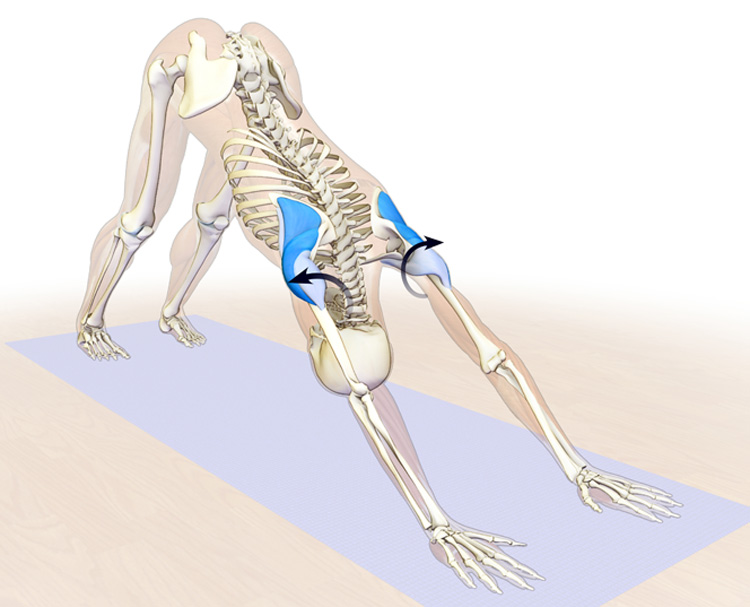
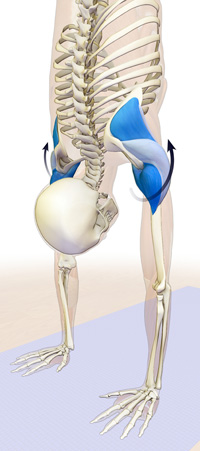
Activate the forearm muscles as described here. Then balance this with external rotation of the humerus, using the infraspinatus and teres minor muscles of the rotator cuff. This creates a coiling effect through the arms as you straighten them (with the triceps). - See more at: http://bandhayoga.com/keys_shoulder2.html#sthash.strSMAZX.dpuf
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий