Rotator Cuff Trigger Points - Supraspinatus
Posted by Team NAT on Apr 01, 2017
Treating Supraspinatus Trigger Points - Dr. Jonathan Kuttner
About Supraspinatus
Latin supra, above; spina, spine
A member of the rotator cuff, which comprises the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. The rotator cuff helps hold the head of the humerus in contact with the glenoid cavity (fossa, socket) of the scapula during movements of the shoulder, thus helping to prevent dislocation of the joint.
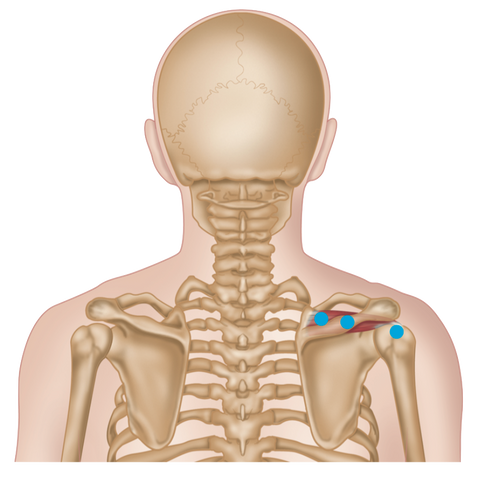 Supraspinatus - Common Trigger Point Sites
Supraspinatus - Common Trigger Point Sites
Origin
Supraspinous fossa of scapula.
Insertion
Upper aspect of greater tubercle of humerus. Capsule of shoulder joint.
Action
Initiates process of abduction
at shoulder joint, so that deltoid can take over at later stages of abduction.
Antagonists: infraspinatus, teres minor, pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi.
Nerve
Suprascapular nerve, C4, 5, 6, from upper trunk of brachial plexus.
Basic Functional Movement
Example: holding a shopping bag away from side of body.
Referred Pain Patterns
Belly: deep ache in regimental badge area (4–6 cm). Ellipse
leads to zone of pain in lateral epicondyle/radial head. Diffuse pain into lateral forearm.
Insertion: localized zone of pain 5–8 cm over deltoid.
Indications
Loss of power in abduction, painful arc syndrome, night pain/ ache, subacromial bursitis, rotator cuff tendinopathy, deep achingin shoulder which can extend to elbow (i.e. tennis elbow) and occasionally to thumb side of wrist, can be confused with De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, pain on initiation of lifting shoulder sideways, inability to reach behind back, moderately restricted range of shoulder motion, clicking/snapping sounds in shoulder joint.
Causes
Carrying heavy objects (e.g. bags, laptops, suitcases) over long distances, heavy lifting from floor to trunk of car, carrying with arms above head, sleeping positions with arms above head, dogs pulling on leash, falls on outstretched arm (e.g. skiing), washing/combing hair, moving heavy furniture, repetitive strain injury (RSI), prolonged computer keyboard use.
Differential Diagnosis
Phase 1 capsulitis. C5–C6 radiculopathy. Subacromial bursitis (adhesive). Calcific tendonitis. Calcium boils. Rotator cuff tendinopathy.
Posted by Team NAT on Apr 01, 2017
Treating Supraspinatus Trigger Points - Dr. Jonathan Kuttner
About Supraspinatus
Latin supra, above; spina, spine
A member of the rotator cuff, which comprises the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. The rotator cuff helps hold the head of the humerus in contact with the glenoid cavity (fossa, socket) of the scapula during movements of the shoulder, thus helping to prevent dislocation of the joint.

Supraspinatus - Common Trigger Point Sites
Origin
Supraspinous fossa of scapula.
Insertion
Upper aspect of greater tubercle of humerus. Capsule of shoulder joint.
Action
Initiates process of abduction
at shoulder joint, so that deltoid can take over at later stages of abduction.
Antagonists: infraspinatus, teres minor, pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi.
at shoulder joint, so that deltoid can take over at later stages of abduction.
Antagonists: infraspinatus, teres minor, pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi.
Nerve
Suprascapular nerve, C4, 5, 6, from upper trunk of brachial plexus.
Basic Functional Movement
Example: holding a shopping bag away from side of body.
Referred Pain Patterns
Belly: deep ache in regimental badge area (4–6 cm). Ellipse
leads to zone of pain in lateral epicondyle/radial head. Diffuse pain into lateral forearm.
leads to zone of pain in lateral epicondyle/radial head. Diffuse pain into lateral forearm.
Insertion: localized zone of pain 5–8 cm over deltoid.
Indications
Loss of power in abduction, painful arc syndrome, night pain/ ache, subacromial bursitis, rotator cuff tendinopathy, deep achingin shoulder which can extend to elbow (i.e. tennis elbow) and occasionally to thumb side of wrist, can be confused with De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, pain on initiation of lifting shoulder sideways, inability to reach behind back, moderately restricted range of shoulder motion, clicking/snapping sounds in shoulder joint.
Causes
Carrying heavy objects (e.g. bags, laptops, suitcases) over long distances, heavy lifting from floor to trunk of car, carrying with arms above head, sleeping positions with arms above head, dogs pulling on leash, falls on outstretched arm (e.g. skiing), washing/combing hair, moving heavy furniture, repetitive strain injury (RSI), prolonged computer keyboard use.
Differential Diagnosis
Phase 1 capsulitis. C5–C6 radiculopathy. Subacromial bursitis (adhesive). Calcific tendonitis. Calcium boils. Rotator cuff tendinopathy.
Rotator Cuff Trigger Points - Supraspinatus
Сообщение от команды NAT на1 апреля 2017
Лечение Supraspinatus Trigger Points - Dr. Джонатан Каттнер
О Supraspinatus
Latin выше , выше; расщелины позвоночника
Член вращающей манжеты, который включает надостный, подостные, Терес Майнор, и подлопаточные. Вращающая манжета помогает удерживать головку плечевой кости в контакте с суставной полостью (ямки, гнездо) лопатки во время движения плеча, таким образом, помогает предотвратить вывих сустава.

Supraspinatus - Общие триггерных Сайты
происхождения
Надостной ямки лопатки.
вставка
Верхняя сторона большого бугорка плечевой кости. Капсула плечевого сустава.
действие
Инициирует процесс похищения
в плечевом суставе, так что дельтовидной может взять на себя на более поздних этапах похищения.
Антагонисты: подостные , Терес Майнор , грудная , широчайшая мышца спины .
в плечевом суставе, так что дельтовидной может взять на себя на более поздних этапах похищения.
Антагонисты: подостные , Терес Майнор , грудная , широчайшая мышца спины .
нерв
Suprascapular нерв, С 4 , 5 , 6 , от верхнего ствола плечевого сплетения.
Основные функциональные движения
Пример: проведение покупки мешок от стороны тела.
Приглашение Patterns боли
Живот: глубокая боль в полковой области бейджа (4-6 см). Эллипс
приводит к зоне боли в боковой надмыщелка / головки лучевой кости. Диффузная боль в боковое предплечье.
приводит к зоне боли в боковой надмыщелка / головки лучевой кости. Диффузная боль в боковое предплечье.
Вставка: локализованная зона боли 5-8 см над дельтовидной.
Показания к применению
Потеря власти в похищении, синдром болезненной дуги, ночные боли / боли, субакромиальной бурсит, вращающей манжеты тендинопатией, глубокое achingin плечо, которое может простираться до локтя (то есть теннисный локоть), а иногда и на стороне большого пальца кисти, можно спутать с тендовагинит де Кервена , боль при инициировании подъема плеча в стороне, неспособность достичь за спиной, умеренно ограниченный диапазон движения плеча, нажав / щелкающий звук в плечевом суставе.
причины
Перенос тяжелых предметов (например , сумки, ноутбуки, чемоданы) на больших расстояниях, тяжелый подъем от пола до багажника машины, неся с рукой над головой, спать позиции с оружием над головой, собаки , тянущее на поводке, падает на вытянутую руке (например , лыжа) , стиральная / расчесывать волосы, перемещаясь тяжелую мебель, повторяющиеся травмы деформации (RSI), длительное использование клавиатуры компьютера.
Дифференциальная диагностика
Фаза 1 тенонит. C5-C6 - радикулопатия. Субакромиальная бурсит (клей). Кальциевые тендинит. Кальций вскипает. Вращающей манжеты тендопатия.
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий